A Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) that originated at South Lhonak Glacial Lake at around 00.40 hours on Oct 4, 2023, washed away the 60 m high dam of Sikkim’s biggest hydropower project, the 1200 MW Teesta 3 HEP. The flood has brought unprecedented disaster all along the river in Sikkim and further downstream in W Bengal and then Bangladesh. Central Water Commission (CWC) reported early in the morning of Oct 4 that there was cloud burst at the site of the lake burst, the cloud burst could have played the role in triggering the lake burst. (Feature image above: A combination of before after photos of Teesta 3 dam put together by Siddharth Agarwal.)
Continue reading “Glacial Lake FLood destroys Teesta-3 Dam in Sikkim, brings wide-spread destruction”Tag: Flood Forecasting
July 2023 Delhi Floods: Why Unprecedented Yamuna Water Levels even at moderate releases?
(Feature Image: Cycles of fisherfolks by the Yamuna and ongoing construction of Metro Bridge downstream of Wazirabad Barrage two weeks before the July 2023 floods. Bhim Singh Rawat/SANDRP, June 28, 2023)
The national capital is witnessing one of the worst flood spells with water level at Railway Bridge breaching the highest recorded 207.49 m of Sept 6, 1978 by 1.17 m. The Yamuna seems eager to reclaim all its relict channel and encroached floodplain areas.
The River has set 208.66 meter as new HFL (Highest Flood Levels) for the site at 18:00 hours on 13 July 2023 which is 1.17 meter higher than the 1978’s HFL. The flood level is receding now.
Continue reading “July 2023 Delhi Floods: Why Unprecedented Yamuna Water Levels even at moderate releases?”Kerala and Uttarakhand floods in Oct 2021: Did the forewarnings help?
The October 2021 flood disasters in two ends of India, in Kerala and Uttarakhand have a lot common. Both happened after the end of normal dates of South West Monsoon 2021. In both cases it is repeat of earlier such disasters in respective states. In both cases, there were reports by expert reports warning about the disasters. In both cases the rainfall events were broadly along the lines warned by the climate scientists, but in both cases the state was ill prepared to cope with it. In both cases, inappropriate human interventions have worsened the disasters in major ways. And in both cases disaster management seems to be absent from ground. In both cases, more precise forecasts about the rainfall quantum and location would have helped. (Feature Image above is from The Hindustan Times, Oct 23, 2021)
Continue reading “Kerala and Uttarakhand floods in Oct 2021: Did the forewarnings help?”Why are Patna & Bhagalpur facing unprecedented floods on India’s 75th independence day?
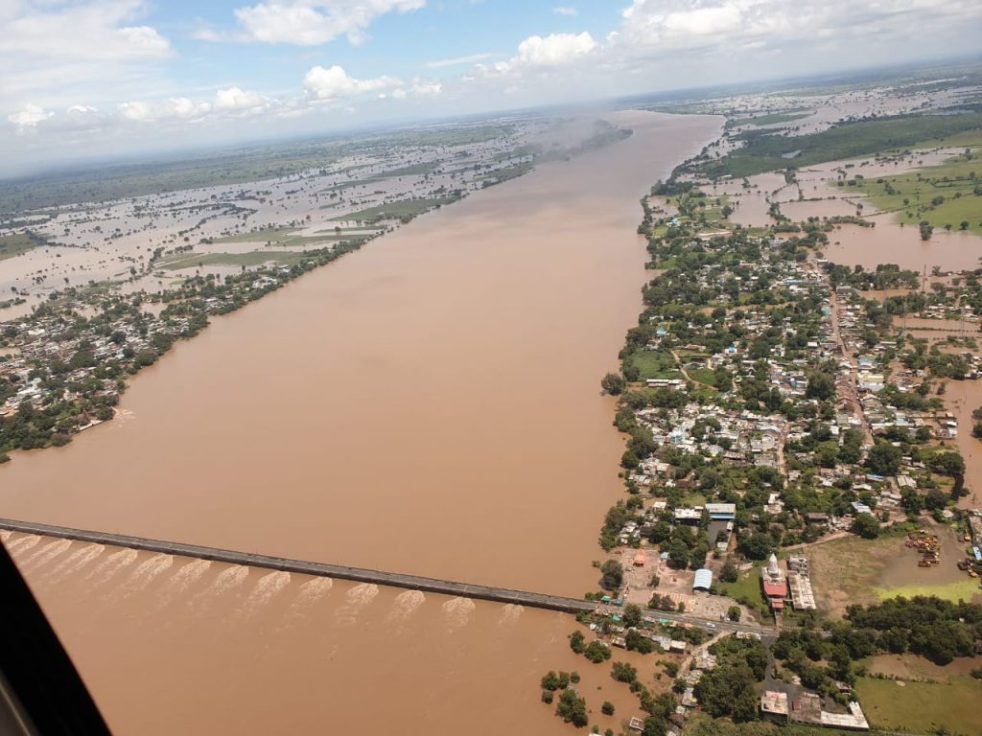
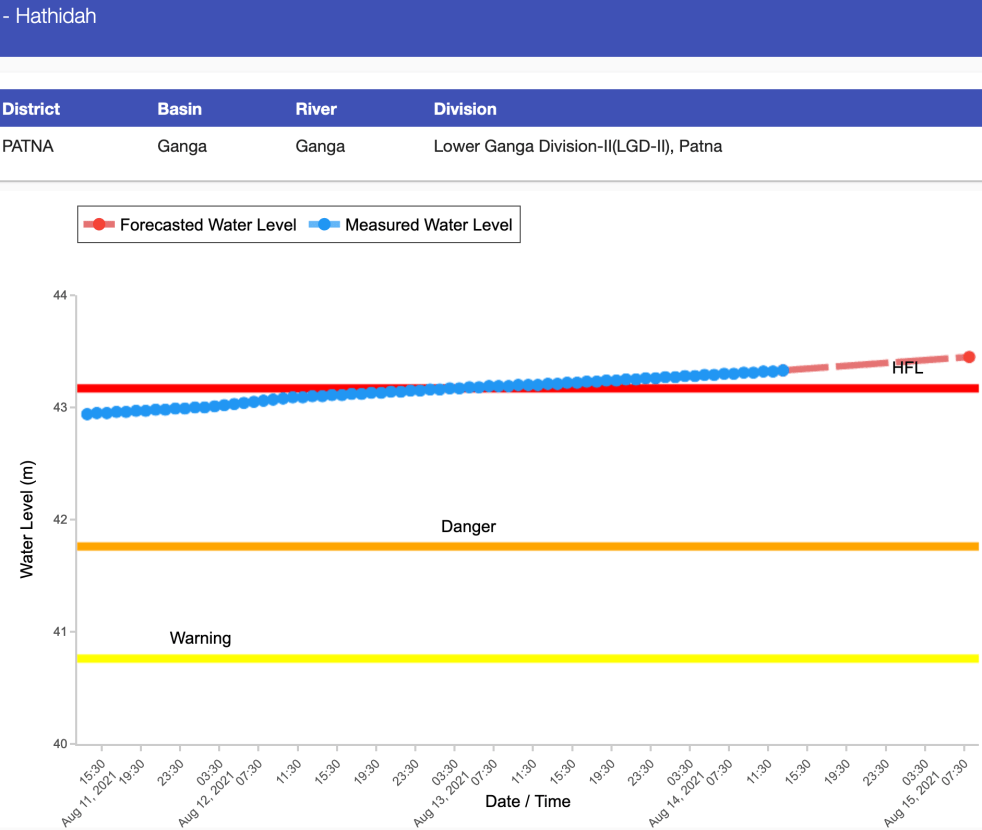
As India prepares to celebrate 75th Independence day on August 15, 2021, large parts of Bihar along the Ganga river, including Patna (flood water entered colonies near Ganga in Patna) and Bhagalpur are preparing to face unprecedented floods. In fact, Central Water Commission’s (CWC) flood monitoring site at Hathidah in Patna district crossed the HIGHEST FLOOD LEVEL (HFL) of 43.17 m at 0300 hours in early morning on Aug 13, 2021. The water level is already at 43.33 m at 1300 hrs on Aug 14. It is forecast to reach 43.45 m by 0800 on independence day still with rising trend. This is apparent from the CWC hydrograph of this site shown above.
Continue reading “Why are Patna & Bhagalpur facing unprecedented floods on India’s 75th independence day?”Rivers That Reached New Highest Flood Level during Monsoon 2020
Flooding in Madhya Pradesh, late August 2020. Photo: MP Govt., flood list.
In 2020, south west monsoon season when rainfall was 8.74% above normal, rivers reached new Highest Flood Levels (HFLs) at least at 37 locations across the country, as per information available to SANDRP. Maximum 13 such instances come from Central and East India, each. Five instances happened in South India, three in North India and two in North East India. This article provides wise details and hydrographs of all these sites.
SANDRP has been tracking the Highest Flood Level (HFL) breach incidents during monsoon season. The analysis of such HFL breaches in 2018 and 2019 are available on our website. In 2018 we had listed 25 such instances though SW Monsoon rainfall was 9.4% below normal. In 2019 we listed 37 such instances when the SW Monsoon rainfall was 10% above normal.
Continue reading “Rivers That Reached New Highest Flood Level during Monsoon 2020”Making sense of 2020 Gandak floods
While Bihar is again facing one of the worse floods this monsoon, one basin in Bihar that has possibly faced the maximum floods is Gandak, as a number of reports[i] have described. The floods in Gandak basin were pretty serious, as embankments along Gandak breached at multiple locations, first on western side (Gopalganj district) starting on July 23-24 night and then on Eastern side (Purbi Champaran district). The flood lead to breaking of three year old HFL (Highest Flood Level) record at Dumariaghat, 19 year old HFL record at Lalganj and most shockingly, 34 year old HFL record at Rewaghat. Continue reading “Making sense of 2020 Gandak floods”
CWC flood forecasting: Inadequate, non transparent, inconsistent
As over 4 million people in the flood prone areas of North East go through second wave of floods and Ganga basin enters the long flood season, nation’s focus should be on one particular agency, Central Water Commission which is not only the only flood forecasting agency, but is also answerable in multiple other ways for the recurring flood disaster. But the flood forecasting of CWC[i] is grossly inadequate, inconsistent and non transparent.
To illustrate, let us look at the available information about CWC’s flood forecasting and compare it with happened in 2019 flood season. Out of 29 sites[ii] (7 level monitoring sites and 22 Lavel forecasting sites) where rivers crossed the previous Highest Flood Level as per CWC’s own hydrographs of last year, CWC has not updated HFL for at least 8 sites so far this year. In case Salavad in Jhalawar district in Rajasthan, on Kali Sindh river, in stead of updating the new HFL, CWC suddenly discovered this year that that the site had higher HFL achieved 35 years ago in 1985, though till last year, it listed 1996 HFL! Continue reading “CWC flood forecasting: Inadequate, non transparent, inconsistent”
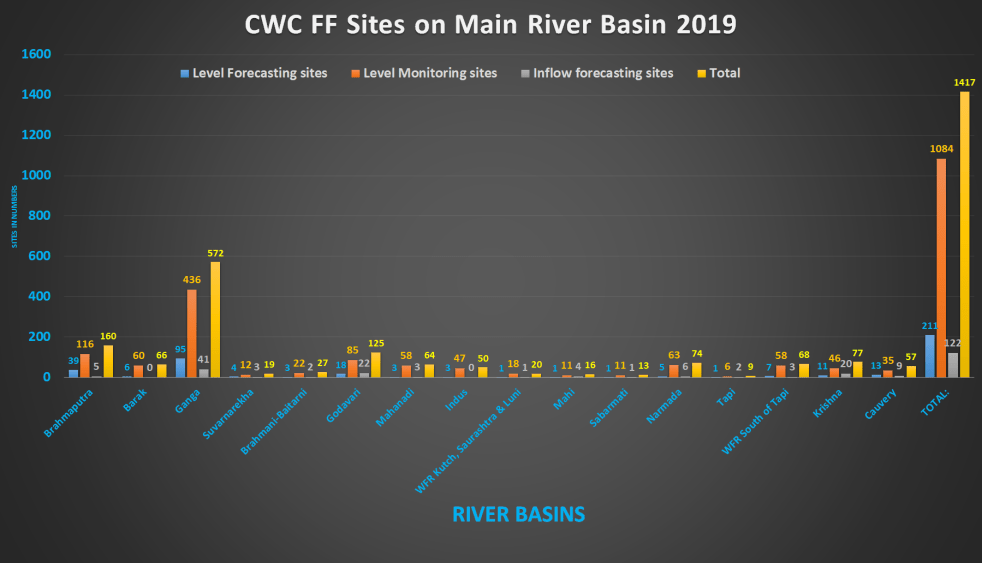
2019 All India summary of CWC flood forecasting sites
This article provides and overview of flood forecasting work of Central Water Commission (CWC) in 2019 after looking closely at each site details for the five regions of India: North East[i], East[ii], North[iii], West[iv] and South[v] India.
The table below provides an overview of number of Level Forecasting, Level Monitoring and Inflow forecasting sites as per CWC’s FF website during 2019 floods for all the states and regions of India.
Continue reading “2019 All India summary of CWC flood forecasting sites”
South India Overview of CWC Flood Forecasting Sites 2019
Flood Forecasting (FF) is one of the important activities of Central Water Commission (CWC), which is undergoing expansion and improvement, but there is still a huge scope for improvement. In order to better understand the CWC’s flood monitoring and forecasting work, in this article, we have given an overview of CWC’s flood forecasting and monitoring sites in South India, the last region to be covered for 2019 flood season. It includes state wise list of CWC’s Level Forecast, Inflow Forecast and level monitoring sites in South Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Puducherry (no FF sites) and Kerala. Similar report has been published for North India[i] and North East India[ii], East India[iii] and West India[iv]. Continue reading “South India Overview of CWC Flood Forecasting Sites 2019”
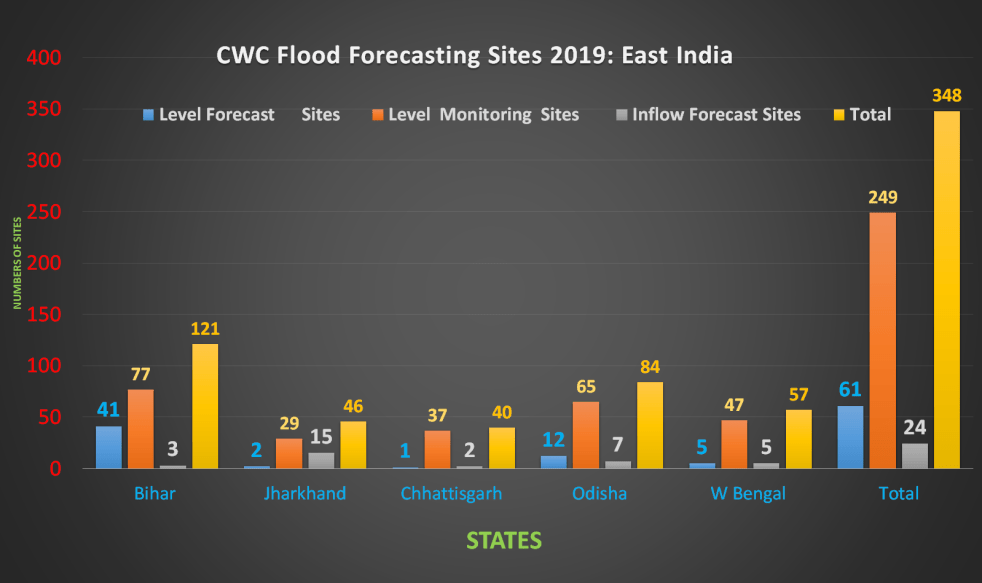
East India: 2019 Overview of CWC Flood Forecasting Sites
Central Water Commission (CWC) is the only agency doing flood forecasting in India. CWC’s Flood Forecasting (FF) is available on its website[I]. In this article we have given an overview of CWC’s flood forecasting and monitoring sites in East India. It includes state wise list of CWC’s Level Forecast, Inflow Forecast and level monitoring sites in East India. Similar report has been published for North East India[II] and North India[III] and we hope to publish reports covering other regions of India soon. East India includes five states: Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhatisgarh, Odisha and W Bengal.
Continue reading “East India: 2019 Overview of CWC Flood Forecasting Sites “