In this second part of the Ganga article, let us listen to some official agencies about the state of Ganga River following the recent efforts.
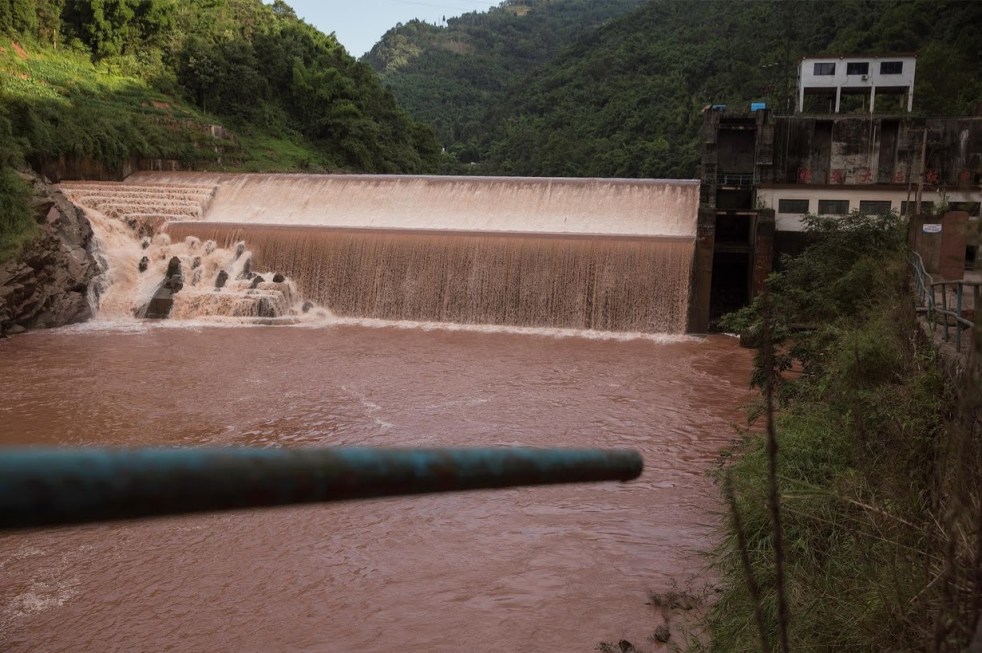
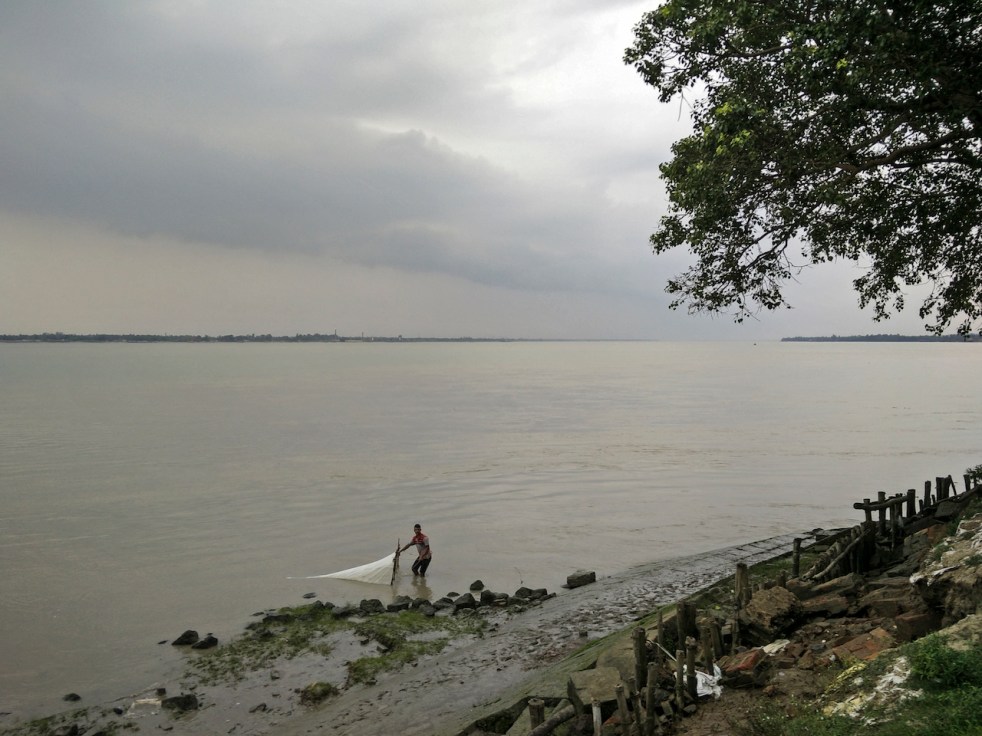
Parliamentary Committee: Why is Ganga among the five most polluted rivers of the world? Said Parliamentary estimates committee (2016-17) for Ministry of Water Resources, Ganga Rejuvenation and River Development (MoWR for short) in a report on “Ganga Rejuvenation” submitted to the Lok Sabha (lower house of India’s Parliament) on 11th May, 2016[i]: “However, indiscriminate anthropogenic interventions like construction of HPPs[ii] in the seismically active and fragile Himalayas, diversion of 80 to 90 percent of water, discharge of extremely hazardous effluents by 144 drains and dumping of solid waste has converted the Ganga into one of the ten most polluted rivers of the world. Alarmed by the drying-polluted Ganga and taking note of the solemn resolve of the Prime Minister to rejuvenate the Ganga, the Committee decided to select the subject for in depth examination and report with a view to accelerate the work of Ganga rejuvenation.” The report also noted, “The Public Accounts Committee (2014-15) in their 8th Report on Water Pollution had expressed distress that the Ganga has become one of the five most polluted rivers in the world, despite launching of the ‘Ganga Action Plan’ and the ‘Mission Clean Ganga’ (2009) by the NGRBA[iii].” Continue reading “Is there hope from National Mission for Clean Ganga? Listen to official agencies”