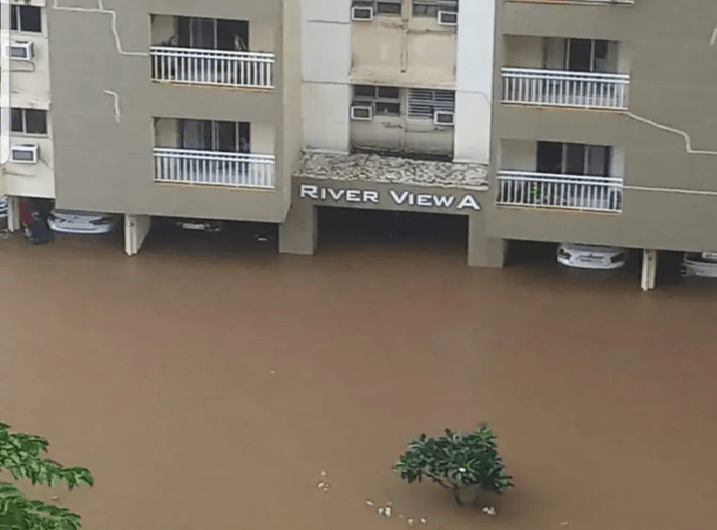
(Feature Image: A flooded housing society in Bangaluru after heavy rainfalls in Sept. 2022)
The excellent opinion piece below by Soumya Sarkar clearly explains how absence of hydrological governance has been root cause for increasing incidents of urban flooding across the country. Indeed, the urban development in India is construction centric where resilience has become a postscript rather an inbuilt feature.
Continue reading “DRP 201025: Indian Cities Drowning in Crisis of Governance”