The earthen Khanda dam in Korea district[i] in Chhattisgarh’s Mahanadi basin breached around 6.30 hrs on Wednesday, Sept 23, 2020. Local farmers alleged negligence by the Water Resources Department officials, who were informed about the dilapidated condition of the dam. The engineers even came and inspected, they said, and went away. They alleged that if they had reduced water storage and in stead opened the two canal gates, this situation may not have come.

Salient Features of the Khanda Dam This is from the CWC’s National Register of Large Dams. (The Google maps have been prepared by Bhim Singh Rawat of SANDRP.)
River Basin: Mahanadi.
River: Not mentioned (from the google map, the dam is on a stream that flows into Gej River, which in turn flows into Mahanadi River downstream Via Atem Nadi and Hasdeo River, the dam is located not too far from the Ridge line separating Mahanadi and Ganga river basins.)
Longitude: 82°36’45” E
Latitude: 23°17’33” N
Year of Completion: 1986
Nearest City: Sonhat
Type: Earthen Dam
Height from the lowest foundation: 10.3 m
Length of Dam: 510 m
Spillway capacity: 59 cumecs (Cumic Meters per second)
Gross Storage capacity: 0.201 MCM (Million Cubic Meters)
Effective Storage Capacity: 0.170 MCM
Reservoir Area: 26.2 ha
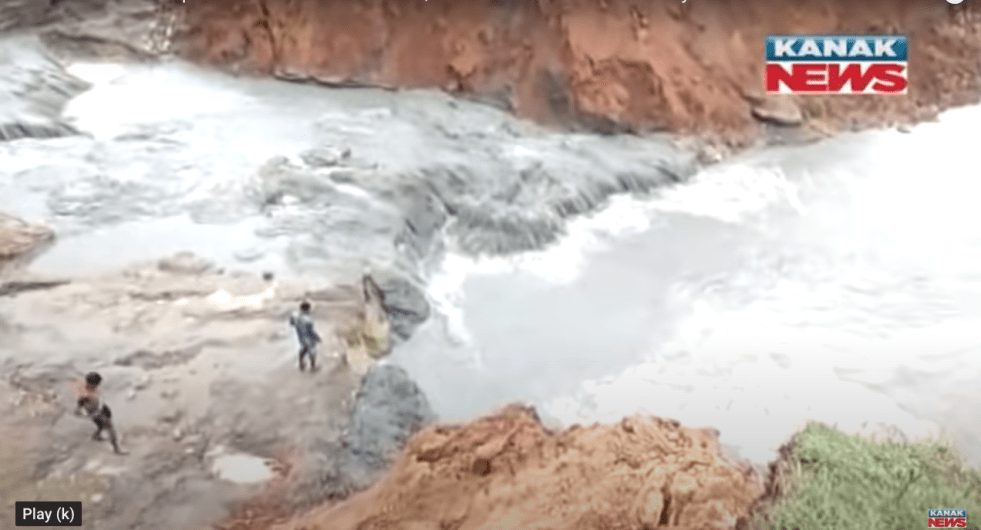
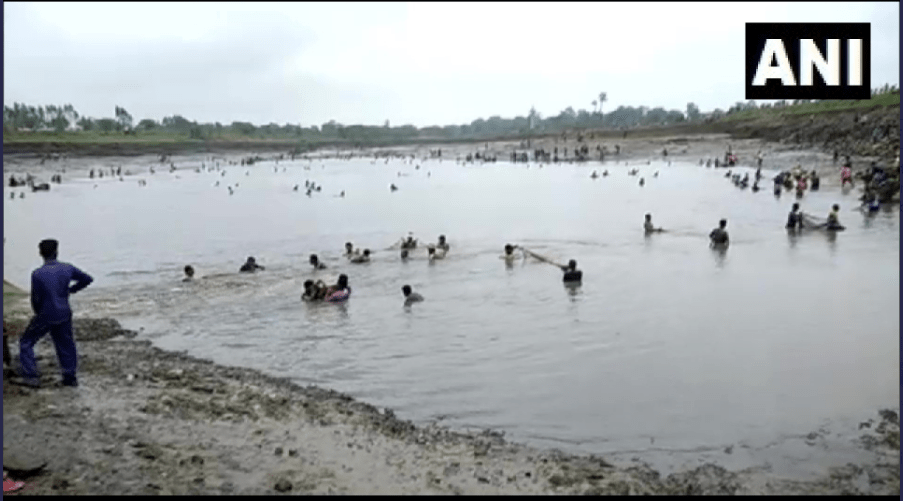
Breach details Very little information is so far available about the breach. “The govt engineer came & surveyed before. We had apprised him of the dilapidated dam but no measure was taken. My entire field’s (five acre) been flattened. How’ll I be compensated now,” says a local farmer.[ii] ANI reported[iii]: “The crop of many farmers has been destroyed by the bursting of the Khanda dam. A video from Kanak News[iv] also provides some visuals and information about the incident. One of the picture ANI shared and included in Kanak News video shows large number of people catching fish in the breached outflow channel and remaining part of the reservoir.
Chhattisgarh water resources department’s official twitter page[v] introduces itself as: “With over a century of experience as a pioneer organization responsible for most of the development works in the Irrigation & Water sector in the State.” It was last updated on Aug 18, 2019, has no information about this dam breach. Same is the situation with their website. IMD reported 7.7 mm rain in Korea district for the 24 hours ending at 0830 hrs on Sept 23, 2020. So rainfall was not a major reason for the breach. From Google map it seems Hathwar dam is in immediate upstream of the Khanda dam.

Vulnerable Earthen Dams It may be noted that Khanda dam was an earthen dam and such dams are much more vulnerable in flood season. National Register of Large Dams lists 258 dams in Chhattisgarh, out of which 255 are earthen dams.
In July 2019, Tiware dam (an Earthen Dam) collapsed in Pune district in Maharashtra[vi], the report of the committee that submitted in Feb 2020 the report of investigation into the collapse is not yet public[vii]. DRIP website (see below) has no word about that disaster.
DRIP website lists 36 dam failures in India till 2010[viii] (so DRIP has not updated list of dam failures for the last nine years), and the highest number (9) failures happened in the latest reported decade of 2001-2010, and all of the nine failures happened at EARTHEN dams. In fact, 30 of the 36 dam failures listed are earthen dam failures. Considering the increased vulnerability of earthen dams particularly in the context of changing climate, there is need for a more comprehensive safety approach for the earthen dams.

The World Bank funded Dam Safety program DRIP is active in Chhattisgarh, but is not help for dams like Khanda Dam? The World Bank has been funding Dam Safety Project in India for quite a few years, it is called DRIP: Dam Rehabilitation and Improvement Project. DRIP is in second phase starting 2019 and includes 736 dams of India out of 5334 large dams. 5 dams from CG are included in DRIP Phas2: Dudhawa Dam (provision of Rs 30 Cr, Commissioned in 1963, 30.53 m high dam and 288.68 MCM gross storage capacity), Moorumsilli Dam (Rs 20 Cr/ 1923/ 34.15 m/ 165.34 MCM), New Rudri Barrage (Rs 7 Cr), Ravi Shankar Sagar Dam (Rs 18 Cr/ 1979/ 30.5 m/ 39.67 MCM) and Sondur Dam (Rs 16 dam, 1989/ 38.2 m/ 198.1 MCM). Out of the five, RS Sagar Dam is Earthen cum Gravity-Masonary dam and New Rudri Barrage is Cement concrete structure, rest are earthen dams.
In Nov 2019 Dam Safety Review Panel has been set up for Chhattisgarh[ix] as part of DRIP project implementation. It is not clear what work DSRP has done so far. The latest available DRIP Bulletin on DRIP website, dated Jan 2020 and pertaining to Oct-Dec 2019[x] quarter (so the bulletins lag about 6-8 months behind, it seems) has just one mention of Chhattisgarh, which interestingly says: “Training on Design flood Review has been carried out in 7 states (Manipur, Meghalaya, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh) by CWC officials as a part of preparatory activities for new DRIP Phase II & Phase III.” It is again unclear if that training in any way helped in possible mitigation of the Khanda dam failure.

Next steps The Standard Operating Procedure adopted by most other dam owning countries is to institute an independent investigation into any such dam mishap. We have proved time and again that such an independent investigation is not something that our water resources establishment believes in. Until and unless we are ready to change that, we are likely to face increasing incidents of dam failures and we are destined to remain largely clueless how to avoid them.
Himanshu Thakkar (ht.sandrp@gmail.com)

END NOTES:
[i] According to https://cgwrd.in/water-resource/wr.html, of the 6605 sq km area of the disgtrict, 4042 sq km is in Ganga basin and remaining 2563 sq km in Mahanadi basin.
[ii] https://www.amarujala.com/chhattisgarh/khanda-dam-burst-in-korea-district-making-flood-like-situation
[iii] https://www.aninews.in/news/national/general-news/flood-like-situation-in-chhattisgarhs-korea-district-after-khanda-dam-bursts20200924095648/
[iv] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xhmpEhJ6dfM
[v] https://twitter.com/wrd_cg
[vi] https://sandrp.in/2019/07/06/tivare-dam-disaster-surviving-in-a-state-with-maximum-dams/
[vii] https://indianexpress.com/article/india/a-year-after-breach-of-tiware-dam-washed-away-hamlet-56-families-wait-on-the-long-road-to-rehabilitation-6486122/
[viii] https://www.damsafety.in/ecm-includes/PDFs/List_Reported_Failure_of_Dams_in_India.pdf
[ix] https://www.damsafety.in/ecm-includes/DRIP_II/DSRP_file/Chattisgarh_DSRP_25Nov2019.pdf
[x] https://www.damsafety.in/ecm-includes/BrochurePhotos/2020DRIPInformationBulletinXIII/DRIPInformationbulletin_13.pdf
