This analysis tracks the decisions taken by Union Ministry of Environment and Forests’ (MoEF) Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC) for River Valley and Hydropower Projects between Jan. 10 and Dec. 19, 2025 regarding Dams, Hydroelectric Power (HEP), Pumped Storage Projects (PSP) and Irrigation related proposals seeking Terms of Reference (TOR) for Environmental Impact Assessments and Environment Clearance (EC) approvals. It also covers various water projects related proposals considered by the MoEF’s Forest Appraisal Committee (FAC) between 27 Jan. to Dec. 02, 2025 for Forest Clearances (FC) approvals. SANDRP’s 2024, 2023, 2022, 2021 and 2020 overviews on the subject can be seen by clicking the hyperlinks.
Continue reading “2025: Env & Forest Clearance Decisions on Dams, Hydro, Irrigation Projects”Tag: Chenab
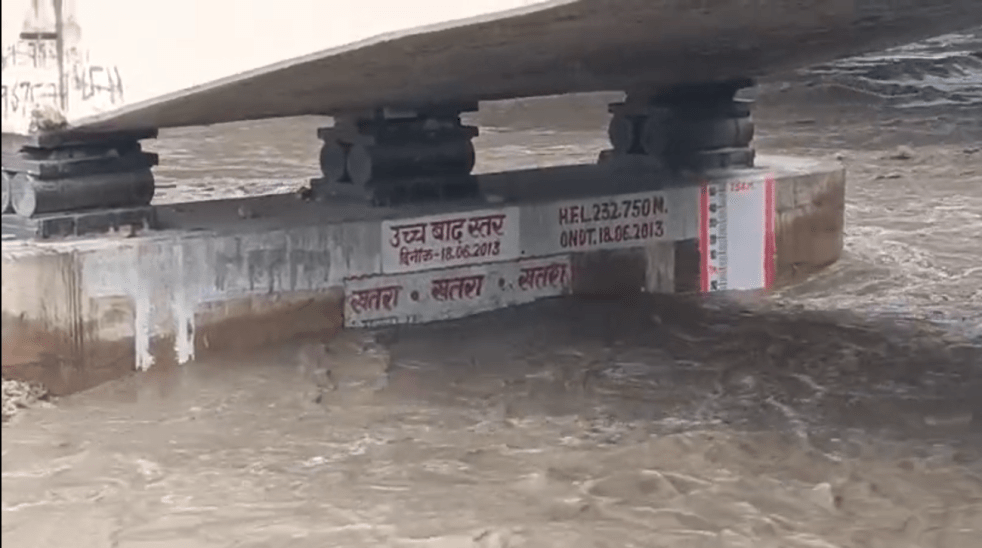
Rivers Flowing in Extreme Floods in September 2025
(Feature Image: Yamuna river in severe flood at Mawi site in Kairana, UP on Sept. 02, 2025)
We have been able to observe river attaining new Highest Flood Level (HFL) at least at 18 flood monitoring sites of the Central Water Commission (CWC) in the last month of South West Monsoon 2025. These 18 sites are spread over 7 States & UT, including Jammu & Kashmir (6 sites), Maharashtra (4 sites), Uttar Pradesh (3 sites), Haryana (2 sites), Madhya Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka (1 each site) comprising 5 river basins including Indus (6), Ganga (6), Krishna (3), Tapi (2) and Godavari (1).
Continue reading “Rivers Flowing in Extreme Floods in September 2025”Vulnerable Nallahs in the Himalayas Need Urgent Attention
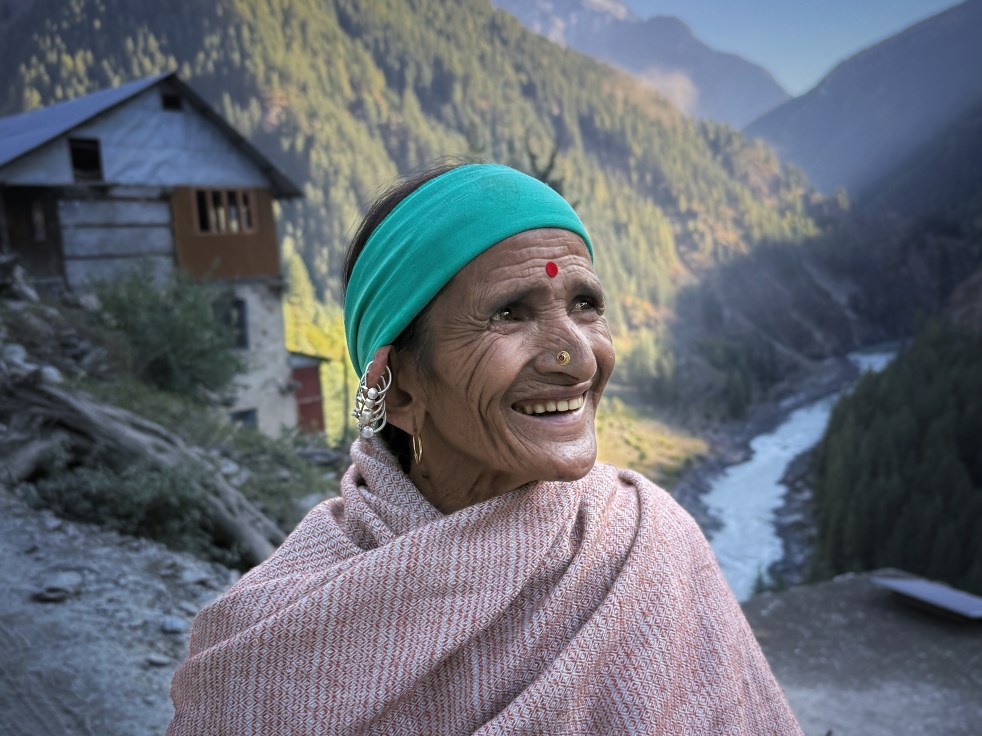
“When Jahlma Nallah starts roaring, we cannot sleep. It has been flooding for the past three years at least” said octogenarian Devi Singhji in October 2024. Jahlma Nallah, which joins the Chenab and blocks it occasionally, flooded again catastrophically in the monsoon of 2025.
Continue reading “Vulnerable Nallahs in the Himalayas Need Urgent Attention”Devastation at Chasoti: Underlining the vulnerability of Chenab Basin again
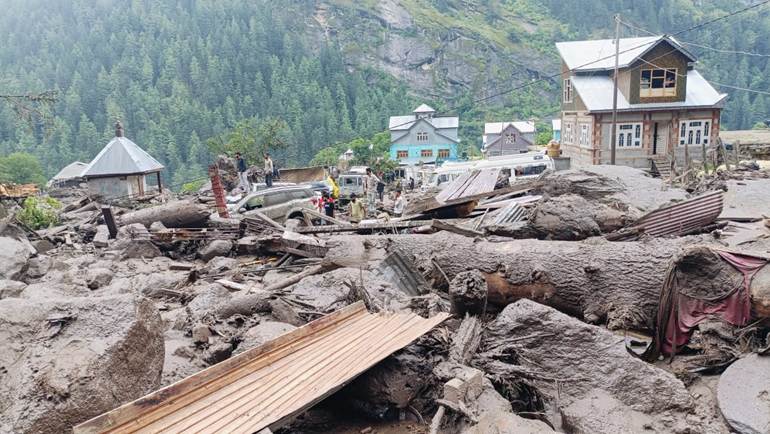
Last October, we were about 15 kms from Chasoti in the Paddar valley of Jammu when we met Dular Singh jee, Priest of Machail Mata Temple, accompanied by other members of the Temple Management Board. They were on their way to Mindhal Mata Temple also on the banks of Chenab in the neighboring Pangi Valley. Theirs was a journey upstream and ours was downstream. We talked of Chenab, floods, Mindhal and Machail Mata Yatra (pilgrimage) and beautifully carved wooden temples of this region.
And today, Dular Singh jee, who is just 3kms from Chasoti, tells me in voice choked with emotion, “I have not seen such a catastrophic flashflood in my life.” The flood that started around 12 noon on Aug 14 2025, devastating Machail Mata yatra and pilgrims at Chasoti. “Mata Rani sabki raksha kare”. (May the deity protect all). He is also worried about villages like “Hangu, Hanoti, Hamori and Bhajanu Nalla”.
Continue reading “Devastation at Chasoti: Underlining the vulnerability of Chenab Basin again”Of Landslides, Spirits and Stories
The Science and Myth surrounding a Himalayan Landslide
Here, in this central spot where three valleys come together
Is the triangle from which all phenomena originate,
An abode of the yoginis of the past,
A place for practitioners in the future.
~ A Tibetan prayer to the sacred Drilbu Ri Mountain where Rivers Chandra and Bhaga meet to form the Chenab
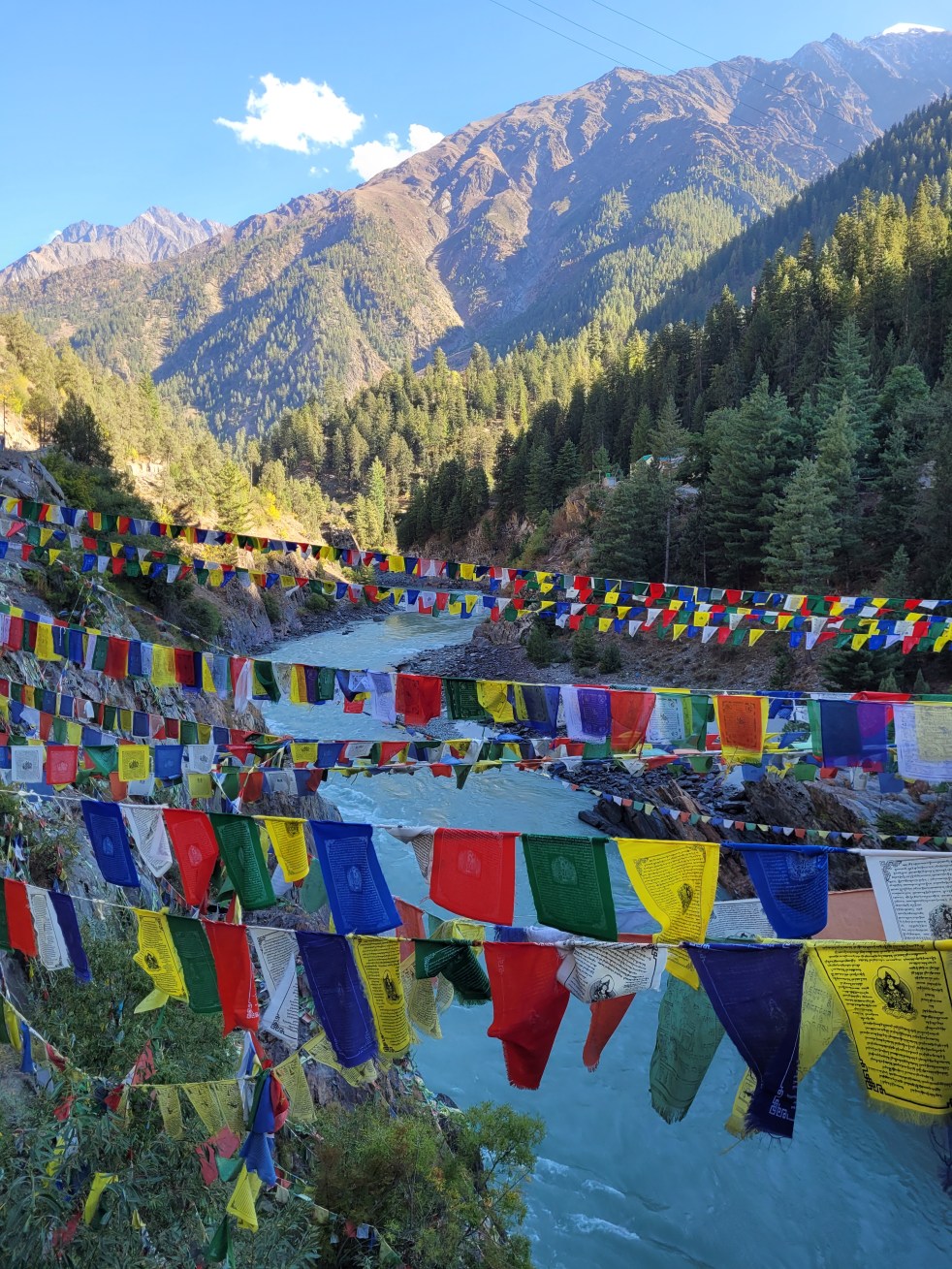
On a crisp September morning, we clank across an iron suspension bridge on the River Chandra to enter the valley of Bhaga. We are tracing the origins of Bhaga and will be reaching Barlacha La pass at an altitude of 15,900 feet in a few hours. Madly fluttering prayer flags swaddling the bridge and the roaring river below make it seem as if, like the prayers, we are adrift on the wind too. Below, on the toasty river sands, a few men doze like monitor lizards.
Continue reading “Of Landslides, Spirits and Stories”Infrastructure Projects in Chenab Basin and Climate Change: Need to Exercise Caution
The current developments around Indus Waters Treaty are deeply troubling. Following the heinous attack on tourists in Pehelgam, India has announced that Indus Waters Treaty, the only water sharing mechanism between India and Pakistan put in place in 1960, has been put in abeyance.
Continue reading “Infrastructure Projects in Chenab Basin and Climate Change: Need to Exercise Caution”A Sinking Village & a Stream that Floods in the Sun: Climate Change, Jahlma Nallah and Lindur in Chenab Basin
At the village of Jasrath in Lahaul and Spiti, the River Chandrabhaga’s current is swift and strong like a rambunctious toddler. The river is new here, birthed just 16 kms upstream at the confluence of the Rivers Chandra and Bhaga. Chandrabhaga will be named as Chenab only after a journey of about 400 kms downstream. Chenab is one of the largest tributaries of the River Indus whose expansive basin feeds over 250 million people in the heart of Asia.
Lahaul and Spiti district in Himachal Pradesh is a cold desert with very little rain, but the narrow ribbons of land along the Chandrabhaga are emerald with willows, apple orchards and cultivated farms. This is precious land.
Continue reading “A Sinking Village & a Stream that Floods in the Sun: Climate Change, Jahlma Nallah and Lindur in Chenab Basin”The Moon River: People’s Story of Chenab
Chenab, which translates as the Moon River is the largest of the five tributaries of River Indus. It flows for about 974 kilometers from the High Himalayas of Lahaul to the forests of Jammu and Kashmir and onto the plains of Pakistan. Its main tributaries in India include Miyar, Marusudhar and Tawi. In the vast plains of Punjab in Pakistan, it is met by Jhelum, Ravi and Sutlej to form the mighty Panjnad before it meets the Indus. Its catchment, spread across 67,430 km2, is shared between the two countries.
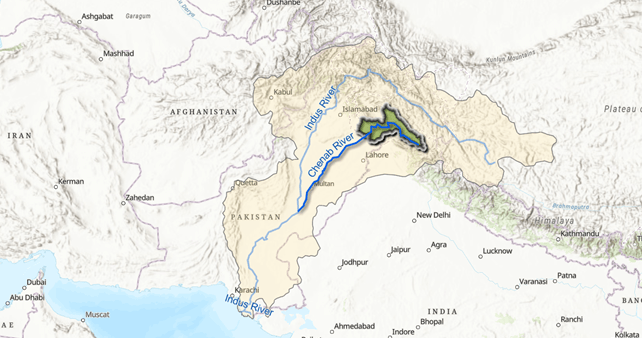
Chenab is Chandrabhaga (Crescent Moon) in its headwaters. It was the River Asikni in Rigveda, and the Acesines for the ancient Greek. From sparse mountain settlements of Lahaul to the bustling urban centers of Sialkot, more than 10 million people live and prosper along the Chenab. Hydropower projects operational and under constructions on the river have an installed capacity of more than 5000 MW (Central Electricity Authority 2024), and its canals irrigate hundreds of thousands of acres in Pakistan and India (Shakir et al).
Continue reading “The Moon River: People’s Story of Chenab”Hydropower-GLOF Nexus in Chenab Headwaters: Absence of credible studies and accountable governance
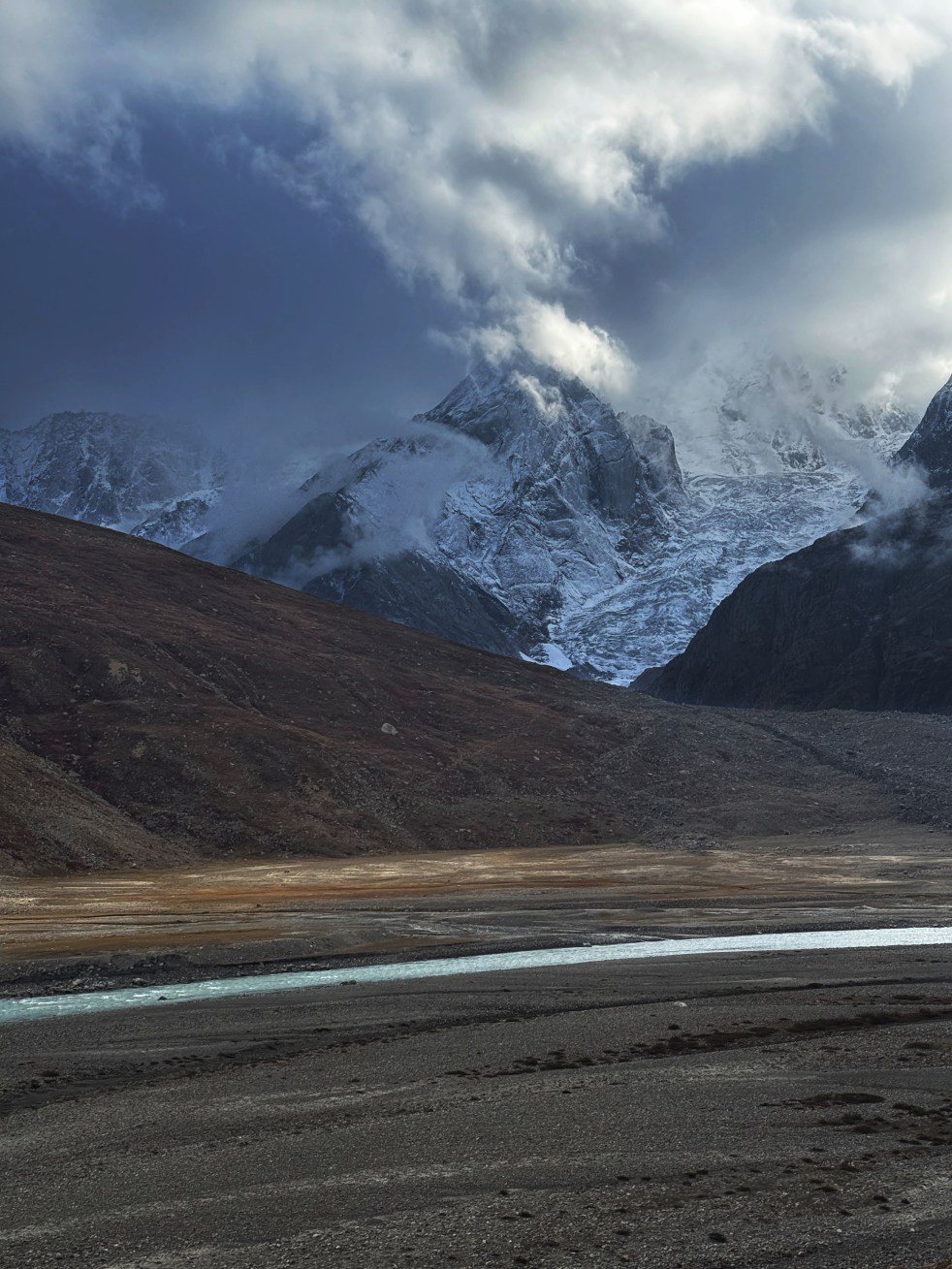
Increasing incidences of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) are being experienced in the Indian Himalayas. One of the most notable examples of GLOF was the Chorabari Lake GLOF that occurred on 16th June 2013 in Kedarnath, Uttarakhand[1] which was triggered by heavy rainfall induced mass movements into the lake. The GLOF devastated villages of Kedarnath, Rambara, and Gaurikund. Around 6,000 people were officially killed, and a significant number of the deaths were linked to the GLOF. Countless bridges and roads were washed away, and about thirty hydropower plants were affected or completely devastated. Several Hydropower projects resulted in exponential losses to life and livelihoods. Whole of Uttarakhand was affected in the disaster, and a significant proportion of it was related with GLOF.
Continue reading “Hydropower-GLOF Nexus in Chenab Headwaters: Absence of credible studies and accountable governance”March 2024: 3 Hydropower Workers Killed in Avalanche in Kinnaur-Himachal Pradesh
(Feature image: Rescue work being done at Selti-Masrang HEP site in Kafnu, Kinnaur on March 11, 2024. Image Source: News 18 Hindi)
A snow avalanche has killed three workers of under construction Selti-Masrang hydroelectric power (HEP) project in Kinnaur district of Himachal Pradesh. The incident occurred in after noon hours reportedly around 01:00 pm on March 11, 2024.
The 24 Mw project is being built by Hyderabad based Ramesh Hydro Power Private Limited on Wangar khad, a tributary of Sutlej River near Kafnu village panchayat in Bhaba valley of the district. The basic information about the project can be seen here. A forest land of 4.75 ha was diverted for the project wide permission given in May 2013. In 2016, 0.64 ha more forest land was applied for. The project cost then in 2016 was Rs 154. 27 cr.
Continue reading “March 2024: 3 Hydropower Workers Killed in Avalanche in Kinnaur-Himachal Pradesh”








