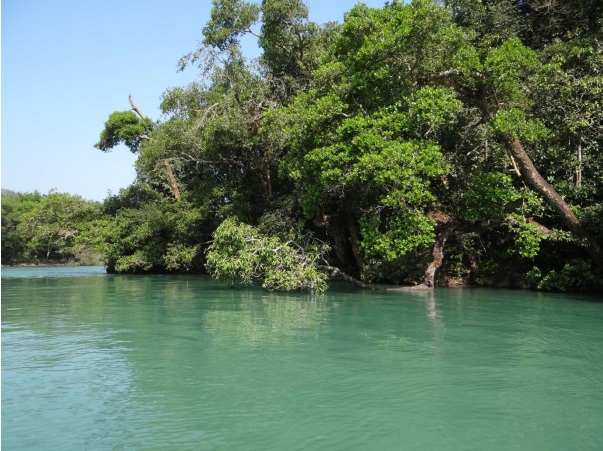
River Kali, before it enters Dandeli in Karnataka is a breathtaking sight..
Its waters are emerald green, flowing steadily. Its banks are thickly forested with a continuous canopy. Endemic species like Malabar Giant Squirrel, Malabar Pied Hornbills, Malabar Gray Hornbills are a common sight here. Down the river, a monitor lizard is stretched across a branch, low over the waters. Fishing eagles and several kinds of Kingfishers look for fish. Fisher folk hover along the banks in beautiful coracles, laying hooks in the riparian vegetation.
During our visit to the Kali, my six-year-old swam in the river and could not believe that the river back in his home-town was once as clear as this!
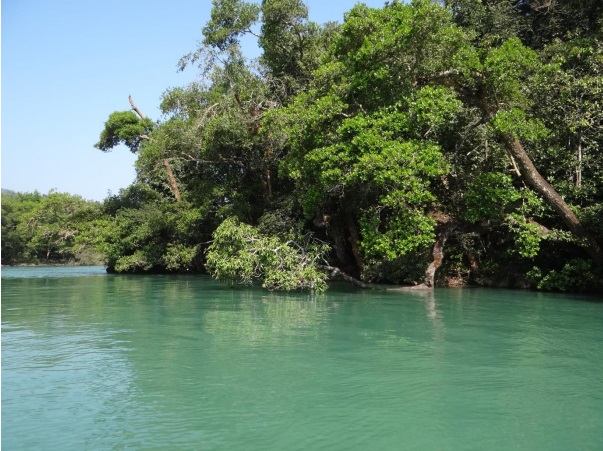

It’s hard to imagine that it was a touch-and-go for this stretch of Kali…
If it were not for some brave, timely advocacy and strong local action, most of this stretch would have been submerged. Rest of the river would have been diverted through a tunnel or silenced in a steady pool of a reservoir: the way many Indian rivers are silenced. There would have been no river, no riparian forests and possibly no swimming.

Dams on Kali: Kali has seen far too much damming. According to Kali Bachao Andolan, a network of organizations working to protect Kali River, more than 5 dams across the river have already submerged 32,000 acres of forests in the Western Ghats. According to Karnataka Power Corporation website, “The west flowing Kalinadi has its origin at an elevation of 900 m, near the DiggiVillage in the Western Ghats of Karnataka. Its 180-km long journey ends at the Arabian Sea near Karwar.”
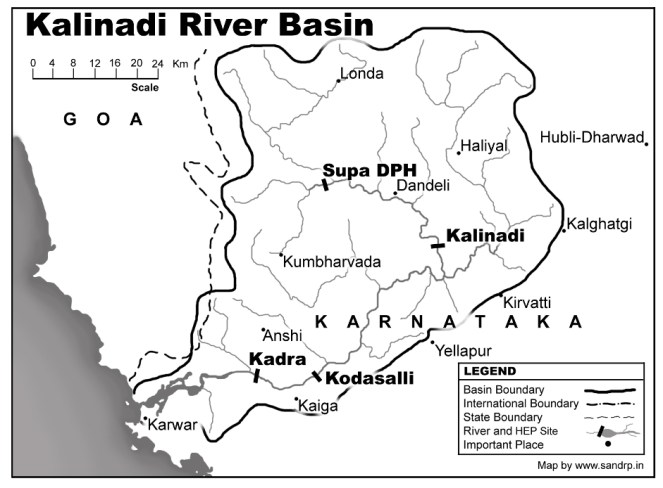
After its origin, it’s dammed at Supa in Joida Taluk of the Uttara Kannada District. The submergence of Supa Dam is a site to behold. Stretching endlessly like an ocean, this dam submerged more than 24 villages and hundreds of hectares of forests. One of the dam evictees, an old, frail man now tells me, “Even now in summers, when the waters recede, I can see my village and my temple. We try to go there some times. I can see all my past life there, for a brief period, before it all goes under water again”.


Downstream the 101 m-high Supa Dam (100 MW), the river flows down through Dandeli town, taking huge pollution from West Coast Paper Mills on the way. From here it is dammed at Bomanhalli Pick up Dam, from where it is diverted to Nagazhari Powerhouse (870 MW), then to Kodasalli Dam and powerhouse (120 MW) and then at Kadra Dam and powerhouse (150 MW). If we look at the flow chart of Kali Nadi Dams, the river seems to be flowing from one reservoir into the next, with nearly no free flowing river stretch between two dams. Its main tributaries Kaneri and Tatihalla have been dammed too.[1] The power generation performance of Kali dams for the last 27 years is shown in the graph above.
There is a stretch downstream the Supa dam to Bomanhalli Pick up dam, where the Kali still flows. This again is controlled flow, regulated by the Supa Dam. But this is the precise stretch which was also targeted to be dammed in 2000’s. An 18 MW project by Murudeshwar Power Corporation Limited (MPCL) was proposed to come up at Mavlangi village downstream Supa Dam. According to Kali Bachao Andolan, it would have meant submergence of 210 hectares of land, including 70 hectares of forest land, next to the Dandeli Sanctuary. Kali Bachao Andolan, including Parisar Samrakshana Samiti, Sirsi and Environment Support Group (ESG), Bangalore, highlighted that Uttar Kannada District only needed 17 MW electricity (in 2000) while it was producing more than 1200 MW electricity and one more dam at a huge social and ecological costs cannot be justified. More importantly, ESG exposed that the Rapid EIA (Environment Impact Assessment) report done by reputed consultancy Ernst and Young for the proponent, was in fact a copy-paste of a different EIA, done by a different agency for a different river! A strong campaign was built around this, which garnered public and media support.

In 2006, the Forest Advisory Committee of the MoEF rejected Forest Clearance for this project. The project was also strongly opposed internally within the Karnataka Government by the Department of Tourism. Surprisingly, MoEF did not book the EIA agent (Ernst and Young) or the proponent (MPCL) for submitting an entirely false report! Even more shockingly, this EIA was later done by TERI (The Energy Research Institute), which also completed the study in one month and came up with a dubious report based on secondary data. However, strong opposition from local groups, ESG, and even within Karnataka Government resulted in rejection of the proposal by a number of authorities, including the Department of Industries and Collectorate of Uttar Kannada. Since then, the project has tried to raise its head again, only to be opposed strongly.[2]

Around 10 years down the line, what does this small stretch of free flowing river mean?
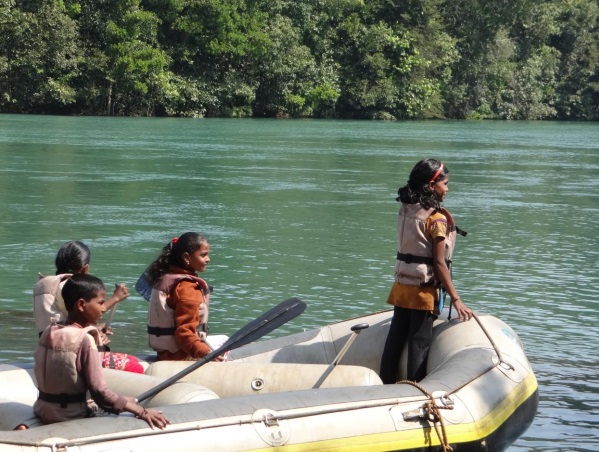
I traveled in Uttara Kannada as a tourist in November 2013. A thriving tourism industry now exists on the banks of Kali and the river is now world-renowned as one of the best rivers for white-water rafting in India. There is boating, canoeing, kayaking, swimming, fishing along this stretch of the river. Pools and islands in the river provide perfect habitats for various species as well as for naturalists and bird watchers. The range of recreational activities that take place along the river are endless. Fishermen still lay their nets across this stretch and catch some fish (though I was told that fish greatly reduced after Supa Dam was commissioned in 1985). Along the banks of the river in this stretch, a thick riparian forest flourishes, providing habitat and corridor to several species.
But more importantly, this tiny stretch is a reminder of how this great river once was. A humbling reminder.
According to Lal, now a boatman and guide from Dandeli, the river stretch which could have been dammed, now provides tourism related employment to around 1000 people from around the region. The region supports around 8 resorts and several homestays. It has created multiple employment opportunities for locals like naturalists, guides, white-water trainers, etc. Some of the locals are descendants of the Supa Dam evictees. One of them says, “The relocated colony of Supa evictees is called Ramnagara, actually it is Vanvasanagara. If it were not for the tourism, I would have migrated to Goa or Belgaon. We saw the fate of Supa dam displaced and would not allow one more dam, no matter how small or big, to affect us again.”
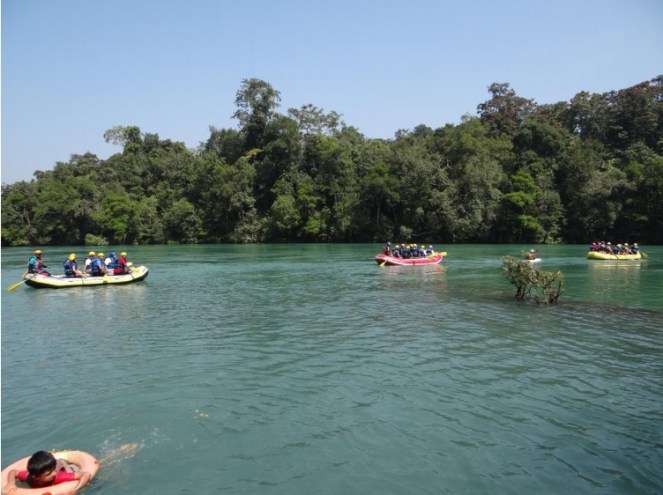

The struggle against 18 MW mini hydel has been significant in a number of ways. EIA and public hearing for the project were the two events where protests were recorded. It was through these platforms that the extent of the impacts of the projects was known and could be opposed. However, after this, a newer version of EIA Notification was adopted in Sept 2006 which excludes hydel projects below 25 MW from its ambit! This has been a ecologically senseless move as projects which have severe impacts on the ecology do not even need a public hearing and an EIA now! We, and several experts and organizations, have raised this point a number of times with the MoEF, but MoEF is yet to respond.
One more strong point of the struggle was a more than 20-year-old order by Karnataka government categorically stating that since the Kali river is so heavily dammed (five major dams on this short 186 kilometre long river, destroying most of its forests and displacing thousands of tribal and forest dwelling communities), no more dams, big or small, shall be allowed further across this river. This has been a very significant order.
Even today, when more and more bumper to bumper dams in the Himalayas and Western Ghats are killing our rivers, our Ministry of Environment and Forests does not have a clear guideline for protecting certain stretches of rivers from dams or declaring them as no-dam stretches. There exists no such order protecting over-dammed, collapsing rivers.The only report which actually recommended that 24 dams in the Upper Ganga basin should be dropped due to their impact on ecosystems, has not been complied with by the MoEF. Dams are coming up in cascades, without leaving any free-flowing riverine stretch between two projects. Nothing is being done about this. The MoEF’s Expert Appraisal Committee on River Valley Projects now has a weak norm of leaving a bare kilometer of flowing river between projects. But this norm too gets twisted and violated.
Avay Shukla committee appointed by Himachal Pradesh High Court recommended that projects should have at least 5 kilometers of free flowing river between them. But MoEF does not seem to support this. In fact, a flowing river seems to have no value in our governance system.
However, as the Kali experience shows, a flowing river is good for ecology and is good for the people too.
Let us take this opportunity to thank the Kali Bachao Andolan and the local communities for protecting the last remaining free flowing stretch of Kali… so that we can catch a glimpse of how a free-flowing river looks like!
– Parineeta Dandekar









