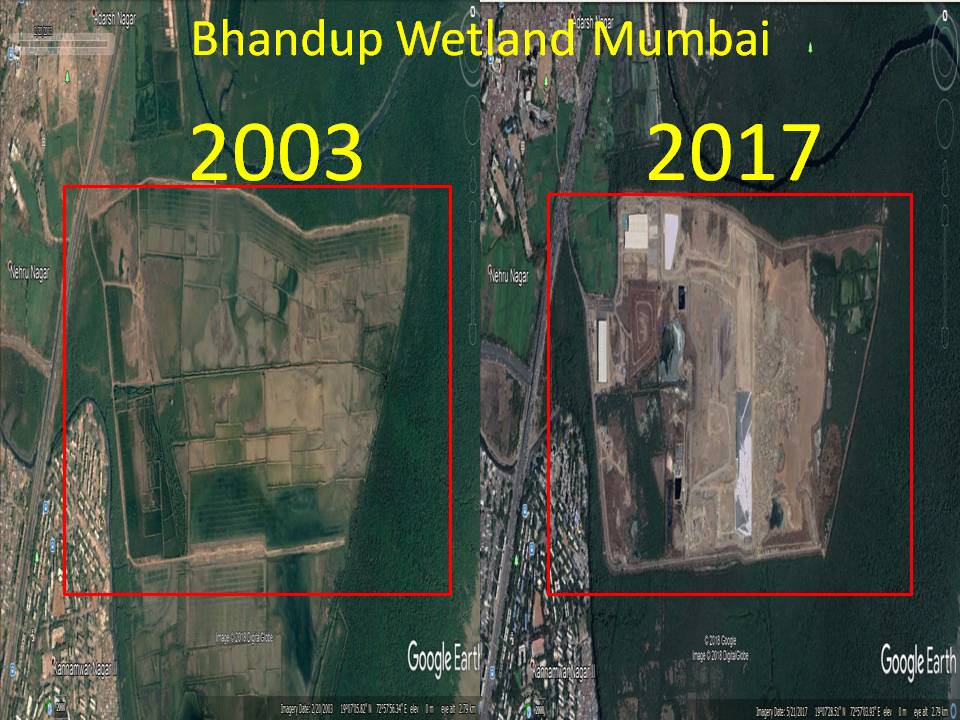
Central Government Decisions
Environment ministry notifies new wetland rules In a major decision, the union environment ministry notified the new Wetland (Conservation and Management) Rules 2017 on 26 Sept. 2017 replacing the 2010 version of the rules. The draft of the Wetland Rules was first presented by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) in March 2016. But they were severely criticized by conservationists who had alleged that the draft rules don’t mention anything about a national regulator and don’t list specific activities prohibited in these ecologically sensitive areas.
The new rules stipulate setting up of a State Wetlands Authority in each State and union territories that will be headed by the State’s environment minister and include a range of government officials. They will also include one expert each in the fields of wetland ecology, hydrology, fisheries, landscape planning and socioeconomics to be nominated by the state government.
The State authorities will also need to prepare a list of all wetlands of the State or union territory within three months, a list of wetlands to be notified within six months, a comprehensive digital inventory of all wetlands within one year which will be updated every ten years.
To oversee the work carried out by States, the rules stipulates for setting up of National Wetlands Committee, which will be headed by the MoEFCC Secretary, to monitor implementation of these rules. The Committee will also advise the Central Government on appropriate policies and action programmes for conservation and wise use of wetlands, recommend designation of wetlands of international importance under Ramsar Convention, advise on collaboration with international agencies on issues related to wetlands etc. http://www.livemint.com/Politics/y6Tr3tkrr3q28AmGKaBFII/Environment-ministry-notifies-new-wetland-rules.html (Live Mint, 28 Sept. 2017)
Continue reading “India Wetlands Review 2017: Important Governments Decisions”