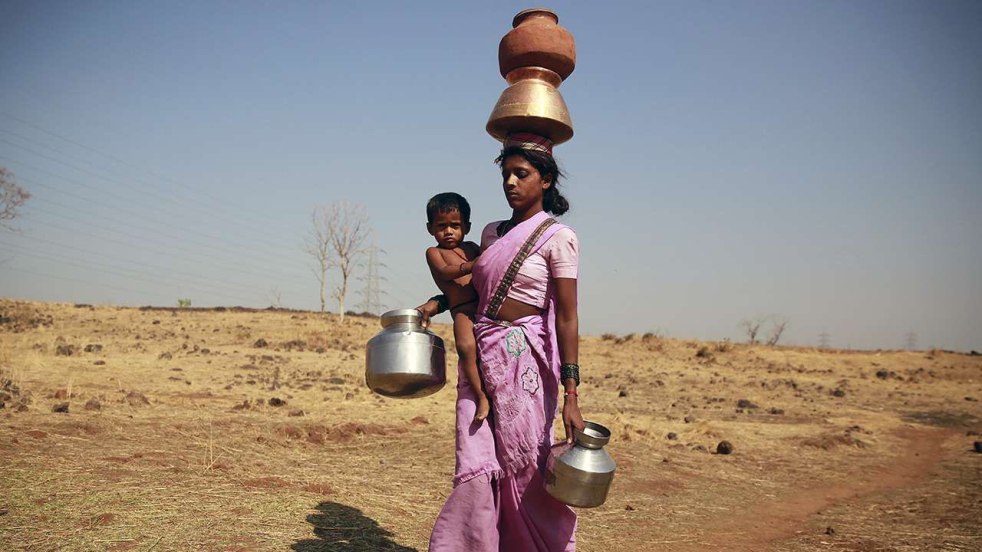
The drought has extended its grip in the South, with the South-West (S-W) monsoon falling significantly short and the North-East monsoon proving a total failure. Reeling under the impact of failed monsoons, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Puducherry have declared themselves as drought affected. Kerala and Karnataka, which are the worst affected, are already contemplating actions such as cloud seeding to tide over the situation.
In Kerala, the S-W monsoon deficit stood at -34 per cent, and the North-East monsoon, -61 per cent. Similarly, in Tamil Nadu, the deficits were -19 per cent and -62 per cent (North-East monsoon). For Coastal Karnataka, the shortfall stood at -21 per cent and -63 per cent, respectively. Drought-like conditions are also prevailing in parts of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
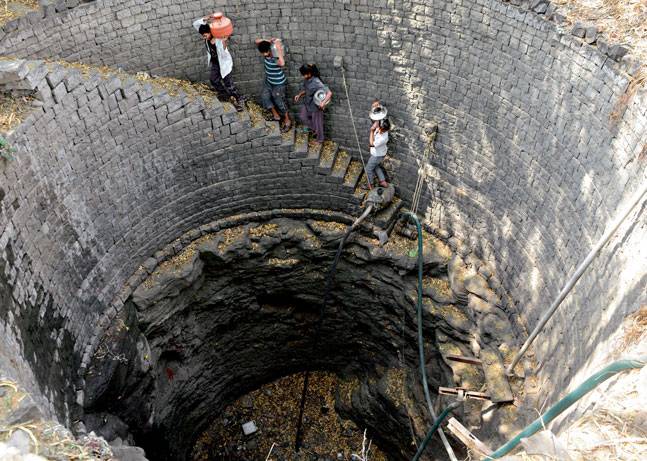
Water levels in key reservoirs in the region are at their lowest. The water tables have declined further even as the civic administration in many cities, small towns and panchayats has been increasingly tapping groundwater to ensure supplies. The situation is so dire that the Kerala govt has directed PepsiCo to cut down drastically on the use of groundwater for its Palakkad plant. Traders in Tamil Nadu are also boycotting these fizzy after claims that foreign firms are exploiting the country’s water resources.
Continue reading “DRP News Bulletin 20 March 2017 (South India Reeling Under Severe Drought)”