Chenab, which translates as the Moon River is the largest of the five tributaries of River Indus. It flows for about 974 kilometers from the High Himalayas of Lahaul to the forests of Jammu and Kashmir and onto the plains of Pakistan. Its main tributaries in India include Miyar, Marusudhar and Tawi. In the vast plains of Punjab in Pakistan, it is met by Jhelum, Ravi and Sutlej to form the mighty Panjnad before it meets the Indus. Its catchment, spread across 67,430 km2, is shared between the two countries.
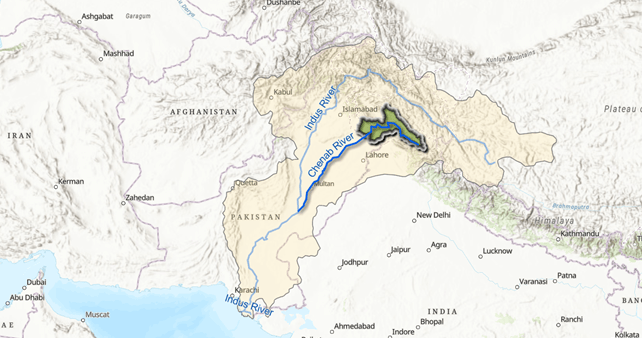
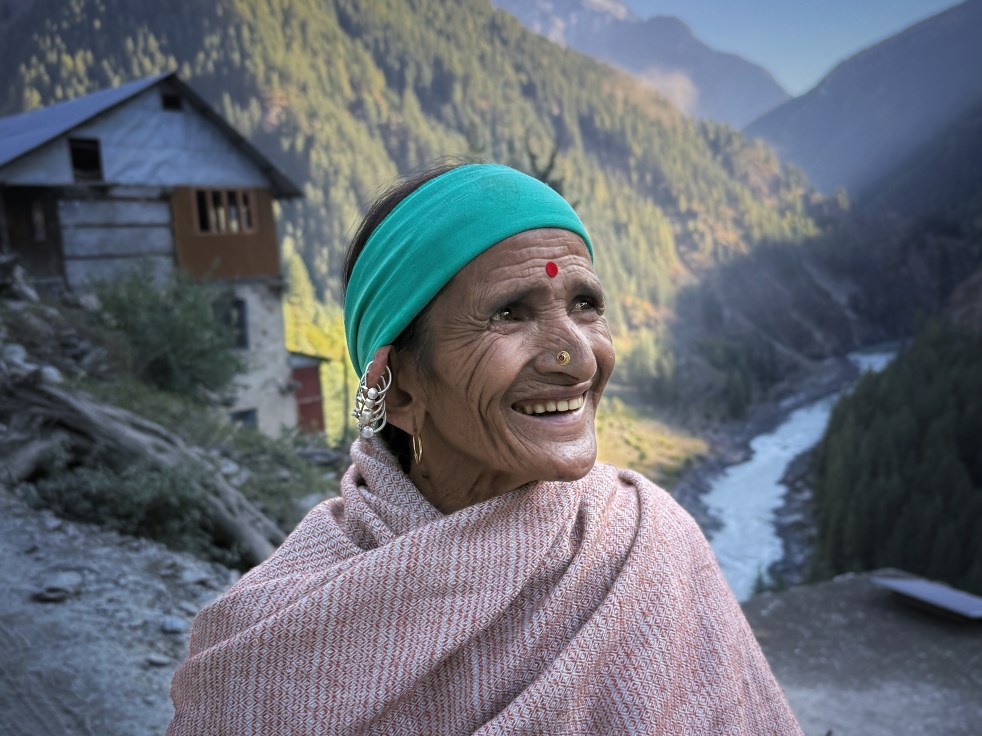
Chenab is Chandrabhaga (Crescent Moon) in its headwaters. It was the River Asikni in Rigveda, and the Acesines for the ancient Greek. From sparse mountain settlements of Lahaul to the bustling urban centers of Sialkot, more than 10 million people live and prosper along the Chenab. Hydropower projects operational and under constructions on the river have an installed capacity of more than 5000 MW (Central Electricity Authority 2024), and its canals irrigate hundreds of thousands of acres in Pakistan and India (Shakir et al).
Continue reading “The Moon River: People’s Story of Chenab”
