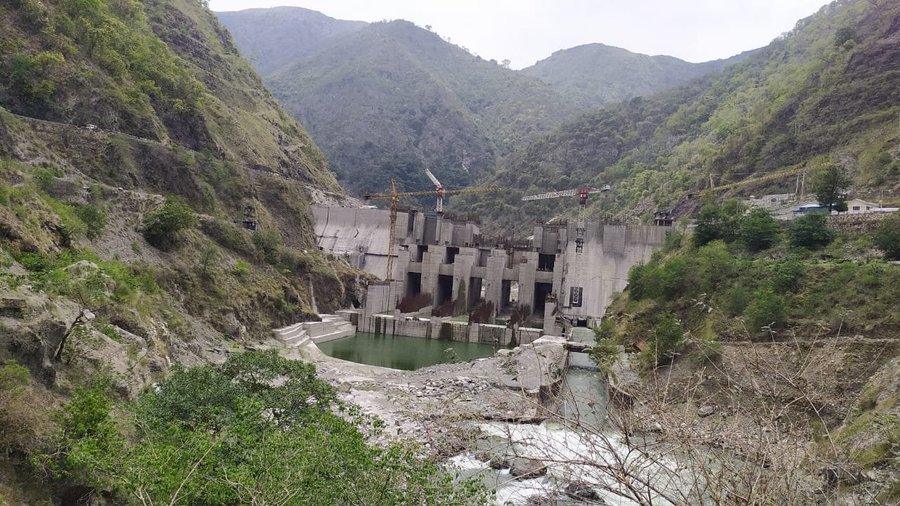
Analyzing a recent paper authored by 37 persons mainly from academics and hydropower related companies on “Sustainable Hydropower”, Eugene Simonov shows why the phrase is an oxymoron, a contradiction in terms. The paper fails to even refer to the most important work on hydropower projects, the report of the World Commission on Dams.
Continue reading “DRP 18 Aug2025: Sustainable Hydropower an Oxymoron?”Tag: GLOF
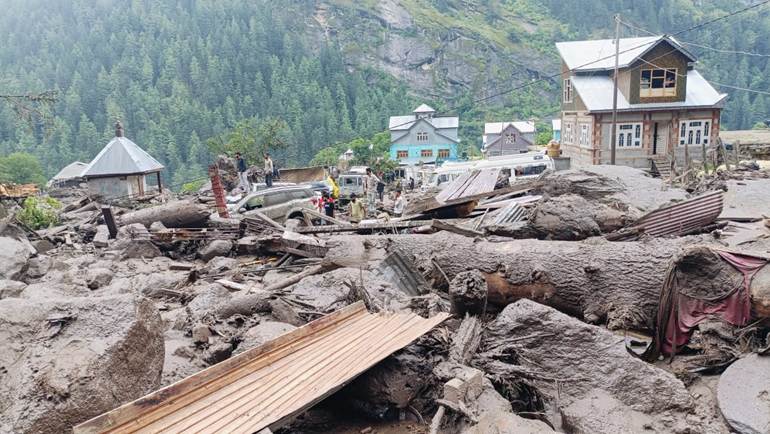
Devastation at Chasoti: Underlining the vulnerability of Chenab Basin again
Last October, we were about 15 kms from Chasoti in the Paddar valley of Jammu when we met Dular Singh jee, Priest of Machail Mata Temple, accompanied by other members of the Temple Management Board. They were on their way to Mindhal Mata Temple also on the banks of Chenab in the neighboring Pangi Valley. Theirs was a journey upstream and ours was downstream. We talked of Chenab, floods, Mindhal and Machail Mata Yatra (pilgrimage) and beautifully carved wooden temples of this region.
And today, Dular Singh jee, who is just 3kms from Chasoti, tells me in voice choked with emotion, “I have not seen such a catastrophic flashflood in my life.” The flood that started around 12 noon on Aug 14 2025, devastating Machail Mata yatra and pilgrims at Chasoti. “Mata Rani sabki raksha kare”. (May the deity protect all). He is also worried about villages like “Hangu, Hanoti, Hamori and Bhajanu Nalla”.
Continue reading “Devastation at Chasoti: Underlining the vulnerability of Chenab Basin again”Dharali Disaster in Uttarakhand: Amplified by Human Causes
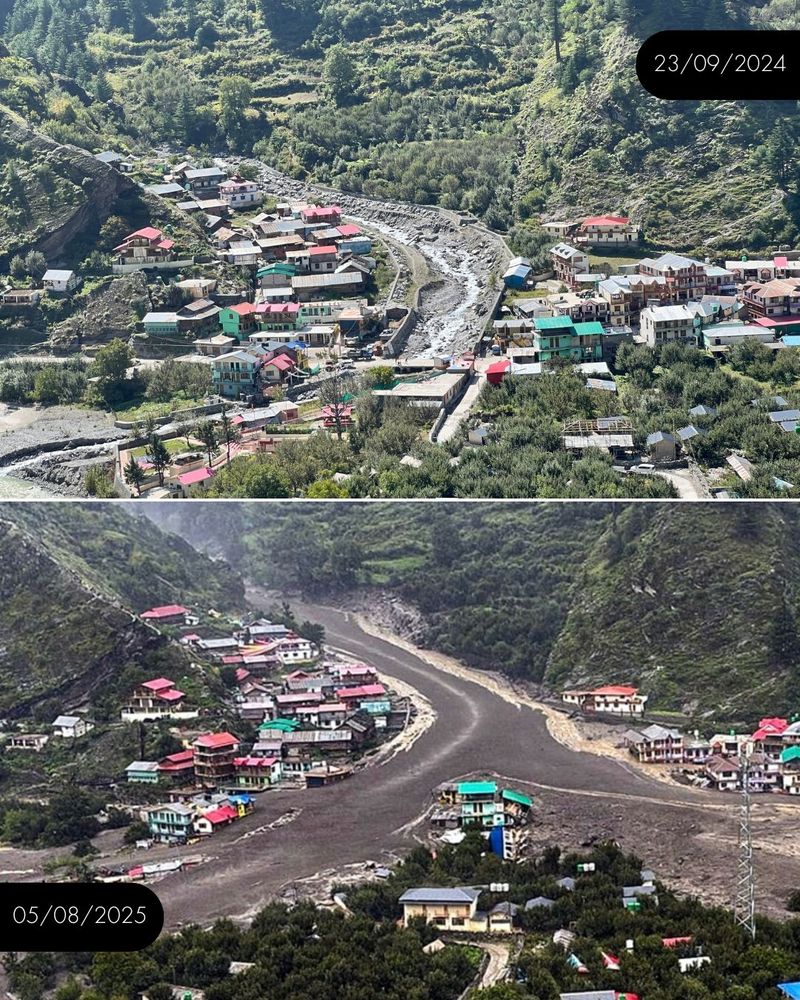
The frightening debris-laden flash flood disaster at Dharali town along Kheer Gad-Bhagirathi river just 20 km downstream of Gangotri at around 1.30 pm on Tuesday, Aug 5 has demolished over 40 buildings, with scores (68 as on Aug 13 as per the Dehradun-based State Emergency Operation Centre) of people, including nine army jawans, reported missing (the numbers could go up as per several geologists) and at least five dead. The ground zero is still largely inaccessible four days after the disaster. While the full details of what caused the disaster are still a bit uncertain, what is clear is that the warning signs were present, they were ignored and a number of human causes amplified the proportions of the disaster. The scene of the disaster was similar to what we saw in Chamoli in Feb 2021 when ice and debris laden stream destroyed two hydropower projects killed over a hundred people.
As geologists said, the disaster was waiting to happen, but our governance did not seem to know.
Continue reading “Dharali Disaster in Uttarakhand: Amplified by Human Causes”DRP 040825: Arunachal Activists urge Centre to find dimensions of China’s Medog Dam
(Feature Image: Aerial view of the Yarlung Tsangpo’s Great Bend, Medog County)
Arunachal and other Himalayan states activists in a press conference in Delhi have rightly urged the Union Government to publicly demand from China all the features and dimensions of the Medog Dam on Yarlung Tsangpo river, their impact assessments and share the same promptly in public domain before even considering any project like the Siang Upper Multipurpose Project (SUMP). This is important since without knowing the features, dimensions, operating procedures and impact assessments, all the projections being made about the possible impacts of the projects are completely speculative and unfounded.
Continue reading “DRP 040825: Arunachal Activists urge Centre to find dimensions of China’s Medog Dam”DRP 280725: CWC Guidelines on GLOF should have mandated all information in public domain, independent assessment after every GLOF
Guidelines for Structural Measures to Mitigate Adverse Effects of GLOF on Dams Central Water Commission (CWC) on July 23 has issued new guidelines to safeguard dam infrastructure from risks and threat of flash floods triggered by glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs). The information about this 40 paged documents named Guidelines for Structural Measures to Mitigate Adverse Effects of GLOF on Dams July 2025 was shared by CWC director Shiv Kumar Sharma, in a LinkedIn post. The document is available in PPT format and a pdf link for the same is still not available.
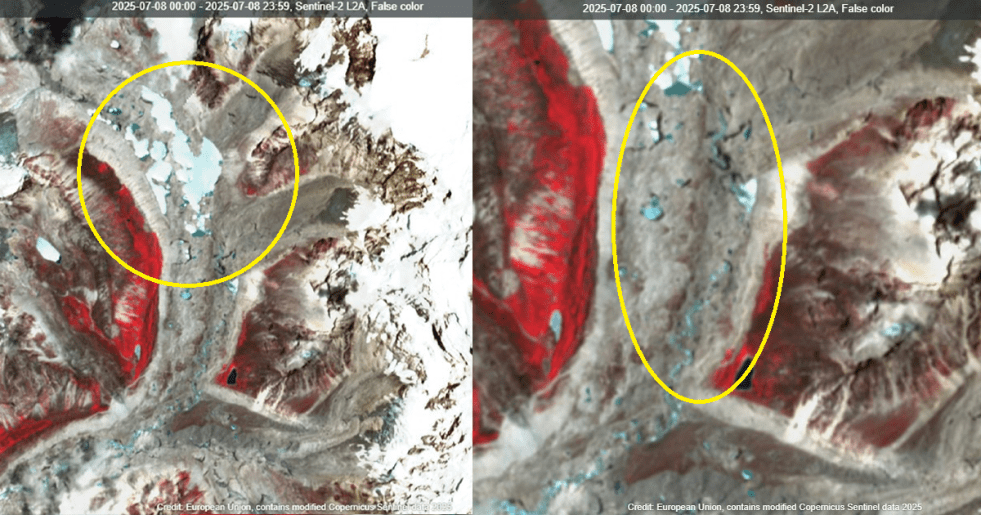
Continue reading “DRP 280725: CWC Guidelines on GLOF should have mandated all information in public domain, independent assessment after every GLOF”July 2025: GLOF Disaster Impact Ten HEPs in Nepal
(Pre and post flood images of Tibet’s Pyurepu Glacier region. Source)
A Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) disaster in Lehende Khola river impacted several hydro-electric power (HEP) projects in Nepal on July 8, 2025. The deadly flood occurred around 3 am in Rasuwa and Nuwakot districts of Nepal bordering Tibet region under China control. As a result, the water level in Lehende river rose by 3.5 meters in Timure, Rasuwa. The merging of Kerung and Lehende rivers in Tibet forms the Bhotekoshi river in Nepal and it is part of Trishuli sub-basin under Narayani river system.
Continue reading “July 2025: GLOF Disaster Impact Ten HEPs in Nepal”DRP 260525: Opposition to large hydro as strategic projects
(Feature Image: Lahaul Spiti Ekta manch holds a protest rally against hydel projects at Udaipur in Lahaul Spiti on Friday May 23. Source: The Tribune)
Some of the most prominent reports this week are related to wide spread opposition to large hydro projects in Arunachal Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Kerala, among other states. Indeed, there is little sense in building large hydro projects as strategic assets as seems to be the case in Himachal Pradesh and J&K (Chenab basin) and Arunachal Pradesh (Siang basin, among others). Use of security forces to complete pre-feasibility survey when local communities are strongly against the project, as is being done in case of Siang Upper Multipurpose Project is clearly counter-productive in so many ways. In Kerala people have again gathered to oppose the destructive Athirapally Hydro projects that they have been successfully opposing since late 1990s.
Continue reading “DRP 260525: Opposition to large hydro as strategic projects”The Moon River: People’s Story of Chenab
Chenab, which translates as the Moon River is the largest of the five tributaries of River Indus. It flows for about 974 kilometers from the High Himalayas of Lahaul to the forests of Jammu and Kashmir and onto the plains of Pakistan. Its main tributaries in India include Miyar, Marusudhar and Tawi. In the vast plains of Punjab in Pakistan, it is met by Jhelum, Ravi and Sutlej to form the mighty Panjnad before it meets the Indus. Its catchment, spread across 67,430 km2, is shared between the two countries.
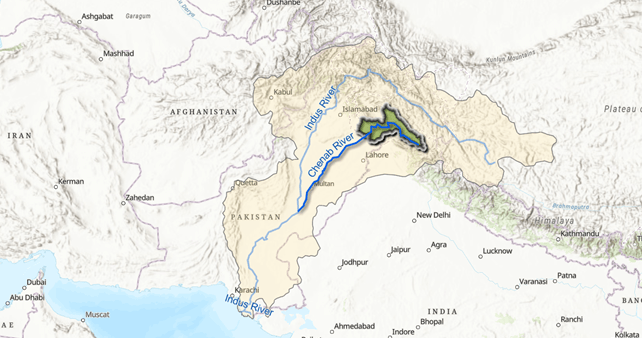
Chenab is Chandrabhaga (Crescent Moon) in its headwaters. It was the River Asikni in Rigveda, and the Acesines for the ancient Greek. From sparse mountain settlements of Lahaul to the bustling urban centers of Sialkot, more than 10 million people live and prosper along the Chenab. Hydropower projects operational and under constructions on the river have an installed capacity of more than 5000 MW (Central Electricity Authority 2024), and its canals irrigate hundreds of thousands of acres in Pakistan and India (Shakir et al).
Continue reading “The Moon River: People’s Story of Chenab”Hydropower-GLOF Nexus in Chenab Headwaters: Absence of credible studies and accountable governance
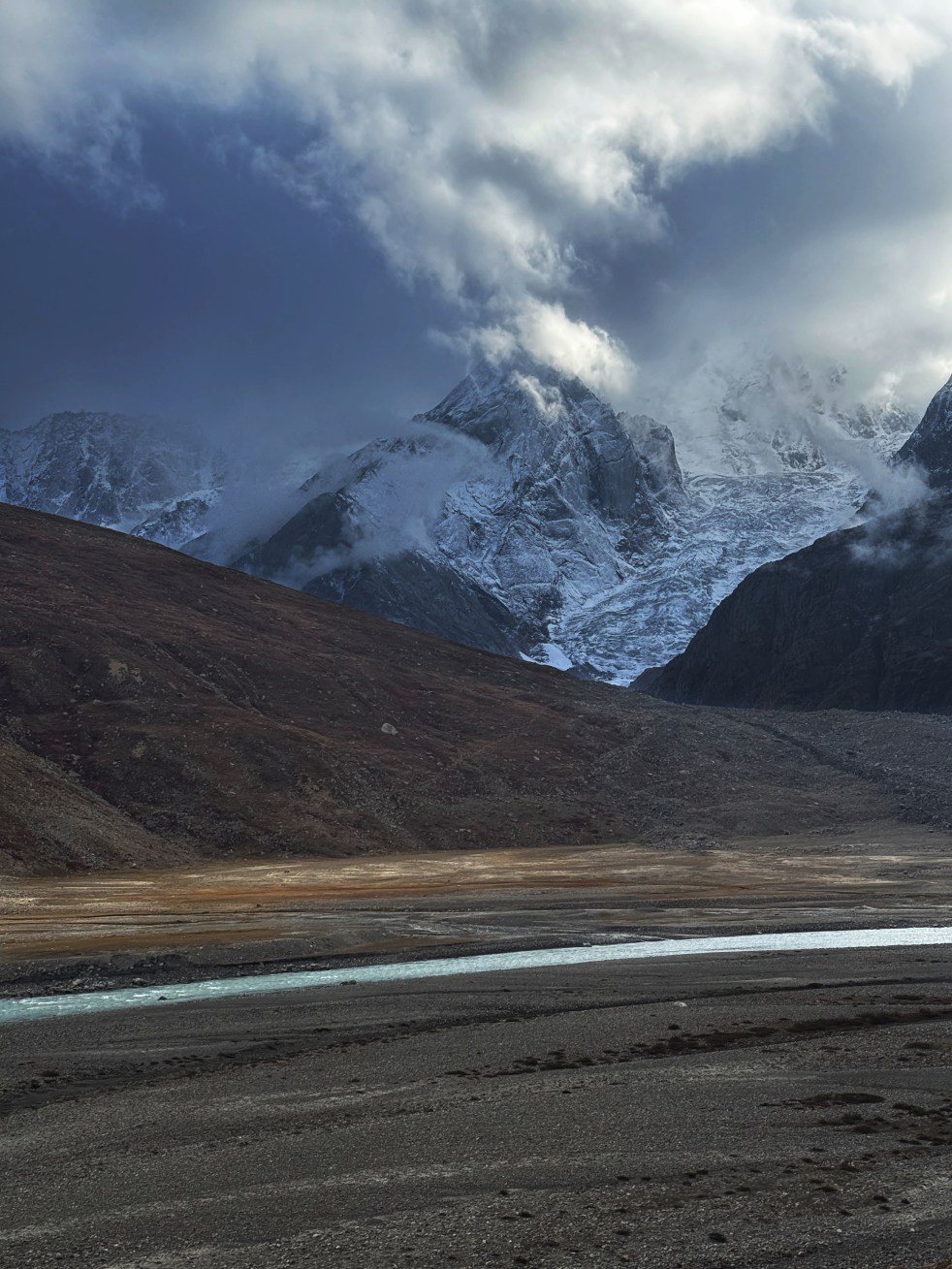
Increasing incidences of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) are being experienced in the Indian Himalayas. One of the most notable examples of GLOF was the Chorabari Lake GLOF that occurred on 16th June 2013 in Kedarnath, Uttarakhand[1] which was triggered by heavy rainfall induced mass movements into the lake. The GLOF devastated villages of Kedarnath, Rambara, and Gaurikund. Around 6,000 people were officially killed, and a significant number of the deaths were linked to the GLOF. Countless bridges and roads were washed away, and about thirty hydropower plants were affected or completely devastated. Several Hydropower projects resulted in exponential losses to life and livelihoods. Whole of Uttarakhand was affected in the disaster, and a significant proportion of it was related with GLOF.
Continue reading “Hydropower-GLOF Nexus in Chenab Headwaters: Absence of credible studies and accountable governance”DRP 100225: EAC & MoEF’s shocking decision to clear Teesta 3 Dam raises a stir
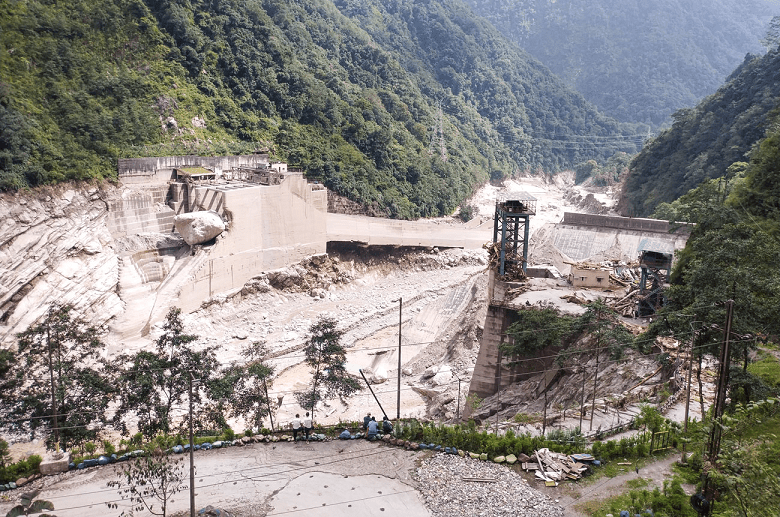
(Feature Image: Teesta III HEP dam was washed away on the intervening night of Oct. 3-4, 2023 on account of a GLOF. The flood in the downstream was magnified by the dam disaster. Photo: Mayalmit Lepcha/Source: Sanctuary Nature Foundation)
The decision of Union Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF)’s Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC) on River Valley Projects on Jan 10 2025 has understandably raised a stir and earlier the EAC and MoEF reviews and reverses this decision, better it will be. The decision is shocking on a number of counts. The EAC itself had raised a number of issues related to the project in its earlier meeting, but decided to clear the project without getting satisfactory resolution of the issues.
Continue reading “DRP 100225: EAC & MoEF’s shocking decision to clear Teesta 3 Dam raises a stir”