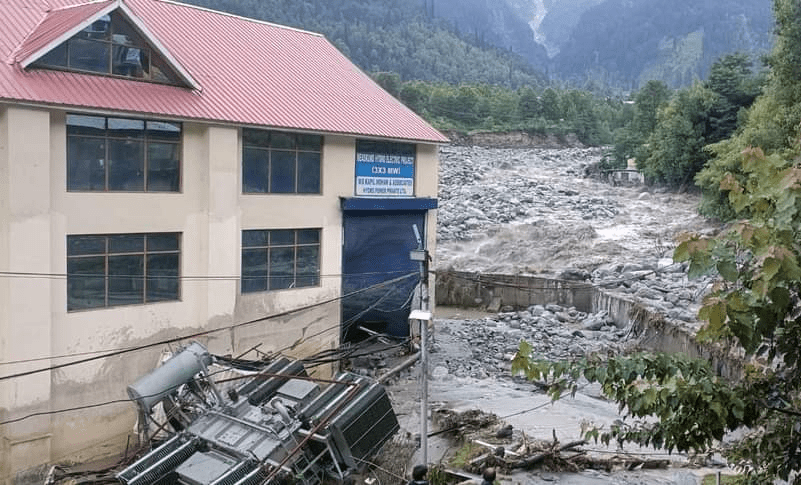
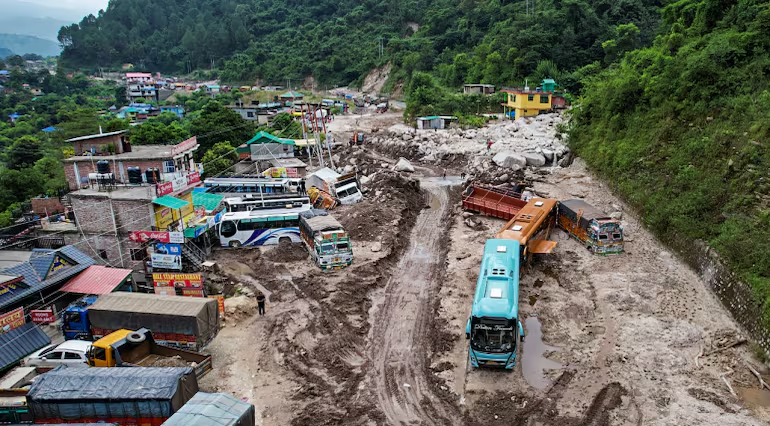
(Feature Image: Vehicles stuck in debris following a recent cloudburst at Saat Meel in Mandi, on August 20, 2023. (PTI Photo/Money Control)
World’s largest democratic exercise is now ongoing in India to elect the members of India’s Lok Sabha. Over 97 crores are eligible to vote in these elections. One of the biggest factors that is adversely affecting people across India currently is Climate Change. It is affecting almost every aspect of life and the adverse impacts are only increasing with every passing year. This is man-made disaster basically happening due to anthropogenic reasons, affecting air, water, climate, food, health, livelihoods, disasters and so on, affecting everyone. Currently, India is also a major contributor to the climate change causing green-house gas emissions, even though historically, the developed countries have contributed much more.
More importantly, the development options that the elected government choose will decide how the people will be impacted by climate change. The government has large number of options for pathways to development. Considering all this, one expected that climate change responses will be a major issue in these elections. But that is clearly not the case. BJP and Congress, two of the biggest parties fighting the elections, have mentioned climate change in their manifestos, but neither has dealt with this important issue with the detail and seriousness required. Nor are any of them making climate change a major election issue. One expects the ruling party to at least respond in greater detail and seriousness to this issue, but that is not the case.
Continue reading “DRP 290424: Why is Climate Change not major election issue?” →